My plan for this week was to go over and talk about IP headers and datagrams. However, while looking through some resources, I find a document that can explain it far better than I can. So instead of diving into the technical nitty-gritty of packets and headers, I'll let Burton Rosenberg of the University of Miami's Computer Science department handy article explain it.
With my original plans for this article taken care of, I instead thought that it would be a good idea to cover how to actually examine a packet and apply this information. It is one thing to know the theory, and another entirely to apply it. With that in mind, I decided to play around with Wireshark and throw together a little demonstration depicting the process.
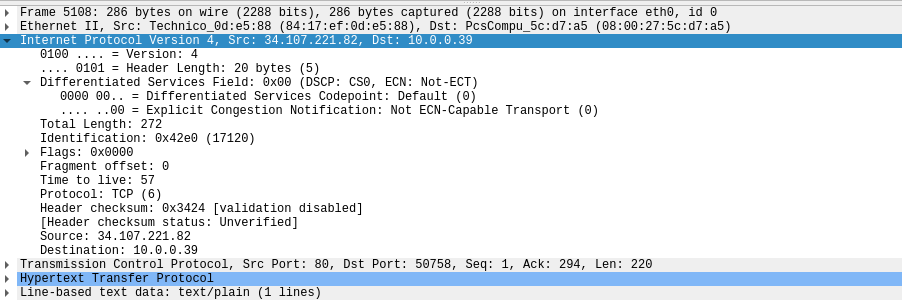
This is a Wireshark window that shows the HTTP traffic to and from my VM. To generate this information, I started Wireshark, confirmed in the capture options that it was using the correct adapter, and performed a google search. The packet that I'll be looking through is a response from one of the searches. When you initially click on it, the packet details and packet bytes viewer are populated.
 |
Packet Detail viewer
|
 |
| Packet Bytes viewer |
While these might look confusing at first, they are easy-to-use tools that can simplify the process of extracting the IP header. In the packet detail field, simply scroll down to the IPv4 or v6 drop-down menu. After opening the menu, you will see each of the fields within the IP segment of the packet as their own submenus. Clicking on any of these will also highlight the corresponding hex values in the packet bytes viewer.
In this image, I have selected the source field in the packet details viewer and the actual bytes have also been highlighted below. Wireshark parses through all of the information for us and provides an easy-to-read format in the packet details viewer. By utilizing Wireshark's built-in tools, it is incredibly easy to find and process IP information and packets.
Comments
Post a Comment